Introduction to Country Context(trT)
|
|
Cameroon is a country of Central Africa; his territory covers nearly 475,650 k m². The country has nearly 590 km of coastline along the Atlantic seaboard and 4591 km of land borders including N igeria in the West (1690 km), Chad in the North East (1094 km), the Central African Republic In the east (797 km), and Congo (523 km), Gabon and Equatorial Guinea (189 km) in the south.
|
|
|
|
Some data and indicators concerning cameroon (trT) |
Distribution of the population by age and Sex (trT)
|
|
The age pyramid shows a broad base and a narrowed top. This triangular shape is characteristic of young populations with high fertility and high mortality rate. In fact, the age group 0-24 years represents 62.5% of the total population. The health policies should prioritize this target in order to benefit from the demographic dividend. The population aged 60 and over is 6.4%.
|
|
|
Health Status and Trends(trT)
Life expectancy at birth (trT)
|
|
Life expectancy at birth in Cameroon was estimated at 54 years in 1990. It rose from 51 years in 2000 to 57.3 years in 2015. In 2015, life expectancy is 2.7 years higher for women than men. Compared to other countries, Cameroon had a better life expectancy at birth than the average for Central African countries (ECCAS) and for Sub-Saharan Africa Respectively 53 and 50 years. 25 years later, the country’s life expectancy at birth is lower than the average for each of the sub-regional groupings (59 years for ECCAS and 60 years for sub-Saharan Africa). Meanwhile, the average life expectancy at birth in the world has increased from 64 years in 1990 to 71.4 years in 2015.
|
|
Burden of diseases and Causes of deaths (trT)
|
|
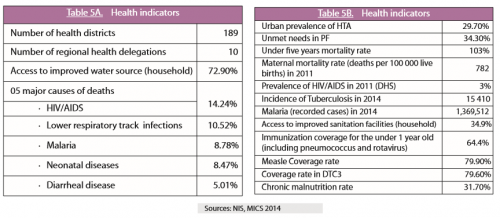
In 2013, Communicable Diseases (CDs) accounted for 40.7% of the burden of disease in Cameroon. (HIV/ AIDS : 11.5% ; malaria : 10.80% ; lower respiratory tract infections : 10.10% ; diarrheal diseases : 5.60%; tuberculosis : 1.40% and STIs : 1.30%. These CDs account for 41.1% of deaths (Global Burden of Disease, 2013).
|
|
|
|
Progress in the Millennium Development Goals(trT)
Global progress in achieving Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) (trT)
|
|
Cameroon adopted the eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). MINEPAT and NIS produced in 2015 a progress report on MDGs and Cameroon has set national targets for 2020, which conclude the ten-year period of the GESP.
This report indicates that the progress of the health MDGs remains mixed. The achievement in the reduction of infant and child mortality rate is 36.89% and 13.75% in the reduction of maternal mortality due to the increase in this ratio between 1990 and 2011.
|
|
|
|
Health-related MDGs focus on maternal health (MDG 5) and child health (MDG 4) and HIV / AIDS, malaria and other diseases (MDG 6). DHS and MICS are the main means for the health system to evaluate its performance.
|
|
Other health-related MDGs. MDG 7 and MDG 8 (trT)
|
|
The nutritional status of children under five years, a measure of poverty reduction, declined between 2004 and 2014. At the same time, the percentage of the population with sustainable access to drinking water increased in both urban and rural areas from 45.30% to 61.00% between 2007 and 2014 (DHS 2011, MICS 2014).
|
|
Other MDG : MDG 1. MDG 2. MDG 3. MDG 7 AND MDG 8 (trT)
|
|
The other MDGs address extreme poverty reduction (MDG 1) establishment of a partnership for development (MDG 8), assurance of primary education for all (MDG 2) promotion of gender equality and women's empowerment (MDG 3), and establishment of a sustainable environment (MDG7).
The incidence of poverty has decreased very little, from 40.2% in 2001 to 37.5% in 2014, a decrease by 2.7 points. We are still far from the 25.1%, the target that was set for 2015 (MDG 1).
|
|
Transition to sustainable development goals (SDGs) (trT)
|
|
In September 2015, countries around the World adopted a common commitment to sustainable development goals (SDGs) by 2030 to replace Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).
SDGs go beyond the MDGs, one of the weaknesses of which was the overestimation of the institutional capacities of the health system to achieve them. The achievement of the SDGs will call for integrated interventions implemented by the various stakeholders in the health sector However, in order to avoid the challenges encountered with the MDGs, Cameroon should necessarily provide SDGs with an operative substance with clear and critical perspectives, underpinned by the search for technical and financial support.
|
|
Health System Performance (trT)
|
|
Cameroon has developed its first Health Sector Strategy 2001-2015 with 6 objectives. An internal evaluation of this strategy, conducted in 2015, showed some progress.
The proportion of the population living within an hour's walking distance of a FOSA is 63.1% in 2013,
with a target of 70% in 2015. Compared with the development of health districts, only 7% have reached
the consolidation stage, for a target of 80% by 2015.
|
|
Leadership and Gouvernance (trT) |
Community Appropriation and Participation (trT) |
Partenarships for Health Dévelopment (trT) |
Health Information, Evidence and Knowledge (trT) |
|
|
Health Financing System (trT) |
Provision of Services and Care (trT) |
Health Human Resources (HHR) (trT) |
Medical Products, vaccines, infrastructure equipement (trT) |
|
|
Universal Health Coverage (trT)
|
Specific Programs and services(trT)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Immunization and Vaccines Development (trT) |
Nutrition, and Child and Adolescent Health (trT) |
Maternal and New-born Health (trT) |
Gender and maternal health (including sexuality and reproductive health) (trT) |
Epidemics and Epidemic-prone diseases (trT) |
Neglected Tropical Diseases (trT) |
Non-Communicable Diseases and conditions (trT) |
Risk Factors for Health (trT) |
|